# Qwen3-TTS
**Repository Path**: github_syn/Qwen3-TTS
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: Qwen3-TTS
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: Apache-2.0
- **Default Branch**: main
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 0
- **Created**: 2026-01-24
- **Last Updated**: 2026-01-24
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# Qwen3-TTS

🤗 Hugging Face | 🤖 ModelScope | 📑 Blog | 📑 Paper
🖥️ Hugging Face Demo | 🖥️ ModelScope Demo | 💬 WeChat (微信) | 🫨 Discord | 📑 API
We release **Qwen3-TTS**, a series of powerful speech generation capabilities developed by Qwen, offering comprehensive support for voice clone, voice design, ultra-high-quality human-like speech generation, and natural language-based voice control. It provides developers and users with the most extensive set of speech generation features available.
## News
* 2026.1.22: 🎉🎉🎉 We have released [Qwen3-TTS](https://huggingface.co/collections/Qwen/qwen3-tts) series (0.6B/1.7B) based on Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz. Please check our [blog](https://qwen.ai/blog?id=qwen3tts-0115)!
## Contents
- [Overview](#overview)
- [Introduction](#introduction)
- [Model Architecture](#model-architecture)
- [Released Models Description and Download](#released-models-description-and-download)
- [Quickstart](#quickstart)
- [Environment Setup](#environment-setup)
- [Python Package Usage](#python-package-usage)
- [Custom Voice Generation](#custom-voice-generate)
- [Voice Design](#voice-design)
- [Voice Clone](#voice-clone)
- [Voice Design then Clone](#voice-design-then-clone)
- [Tokenizer Encode and Decode](#tokenizer-encode-and-decode)
- [Launch Local Web UI Demo](#launch-local-web-ui-demo)
- [DashScope API Usage](#dashscope-api-usage)
- [vLLM Usage](#vllm-usage)
- [Fine Tuning](#fine-tuning)
- [Evaluation](#evaluation)
- [Citation](#citation)
## Overview
### Introduction
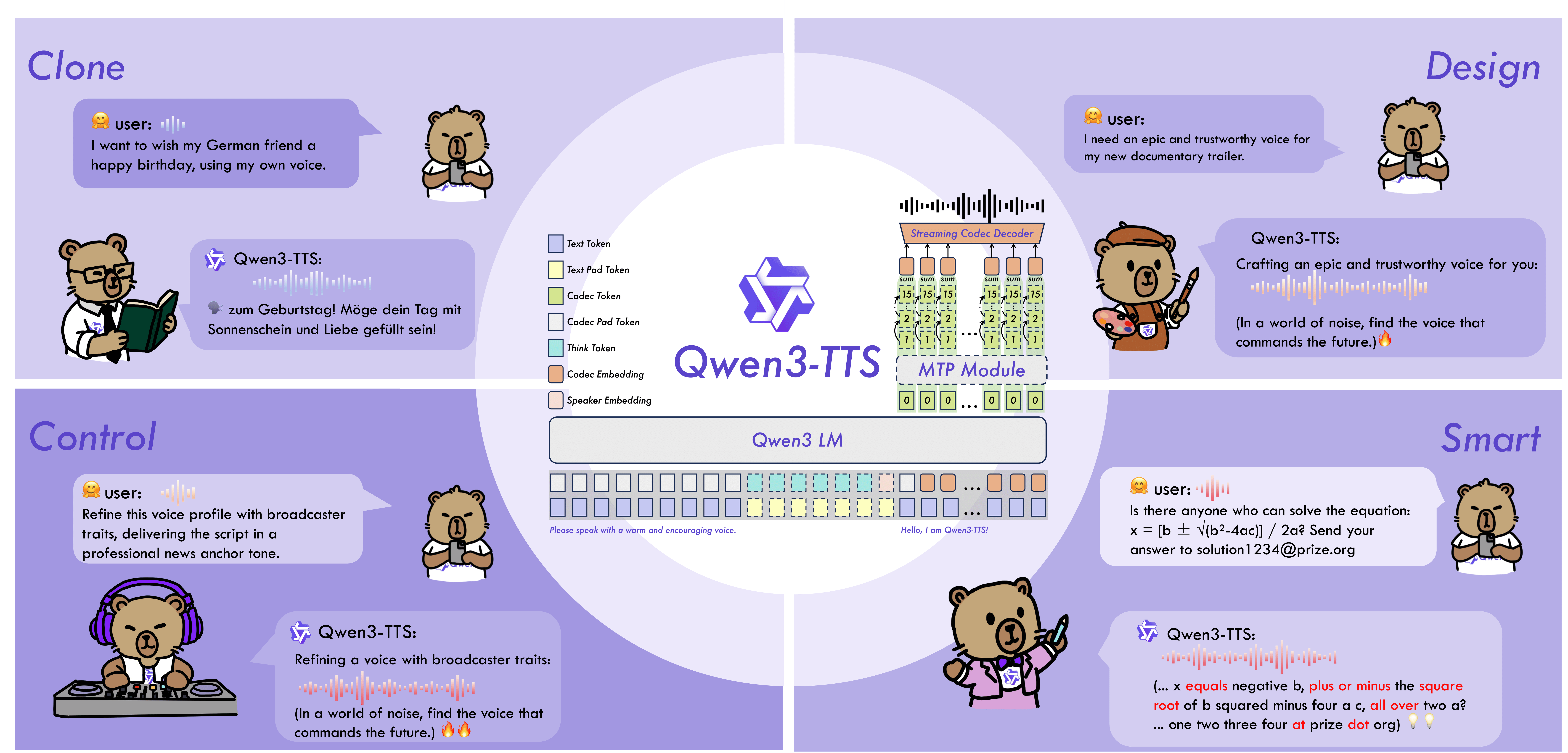
Qwen3-TTS covers 10 major languages (Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, French, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian) as well as multiple dialectal voice profiles to meet global application needs. In addition, the models feature strong contextual understanding, enabling adaptive control of tone, speaking rate, and emotional expression based on instructions and text semantics, and they show markedly improved robustness to noisy input text. Key features:
* **Powerful Speech Representation**: Powered by the self-developed Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz, it achieves efficient acoustic compression and high-dimensional semantic modeling of speech signals. It fully preserves paralinguistic information and acoustic environmental features, enabling high-speed, high-fidelity speech reconstruction through a lightweight non-DiT architecture.
* **Universal End-to-End Architecture**: Utilizing a discrete multi-codebook LM architecture, it realizes full-information end-to-end speech modeling. This completely bypasses the information bottlenecks and cascading errors inherent in traditional LM+DiT schemes, significantly enhancing the model’s versatility, generation efficiency, and performance ceiling.
* **Extreme Low-Latency Streaming Generation**: Based on the innovative Dual-Track hybrid streaming generation architecture, a single model supports both streaming and non-streaming generation. It can output the first audio packet immediately after a single character is input, with end-to-end synthesis latency as low as 97ms, meeting the rigorous demands of real-time interactive scenarios.
* **Intelligent Text Understanding and Voice Control**: Supports speech generation driven by natural language instructions, allowing for flexible control over multi-dimensional acoustic attributes such as timbre, emotion, and prosody. By deeply integrating text semantic understanding, the model adaptively adjusts tone, rhythm, and emotional expression, achieving lifelike “what you imagine is what you hear” output.
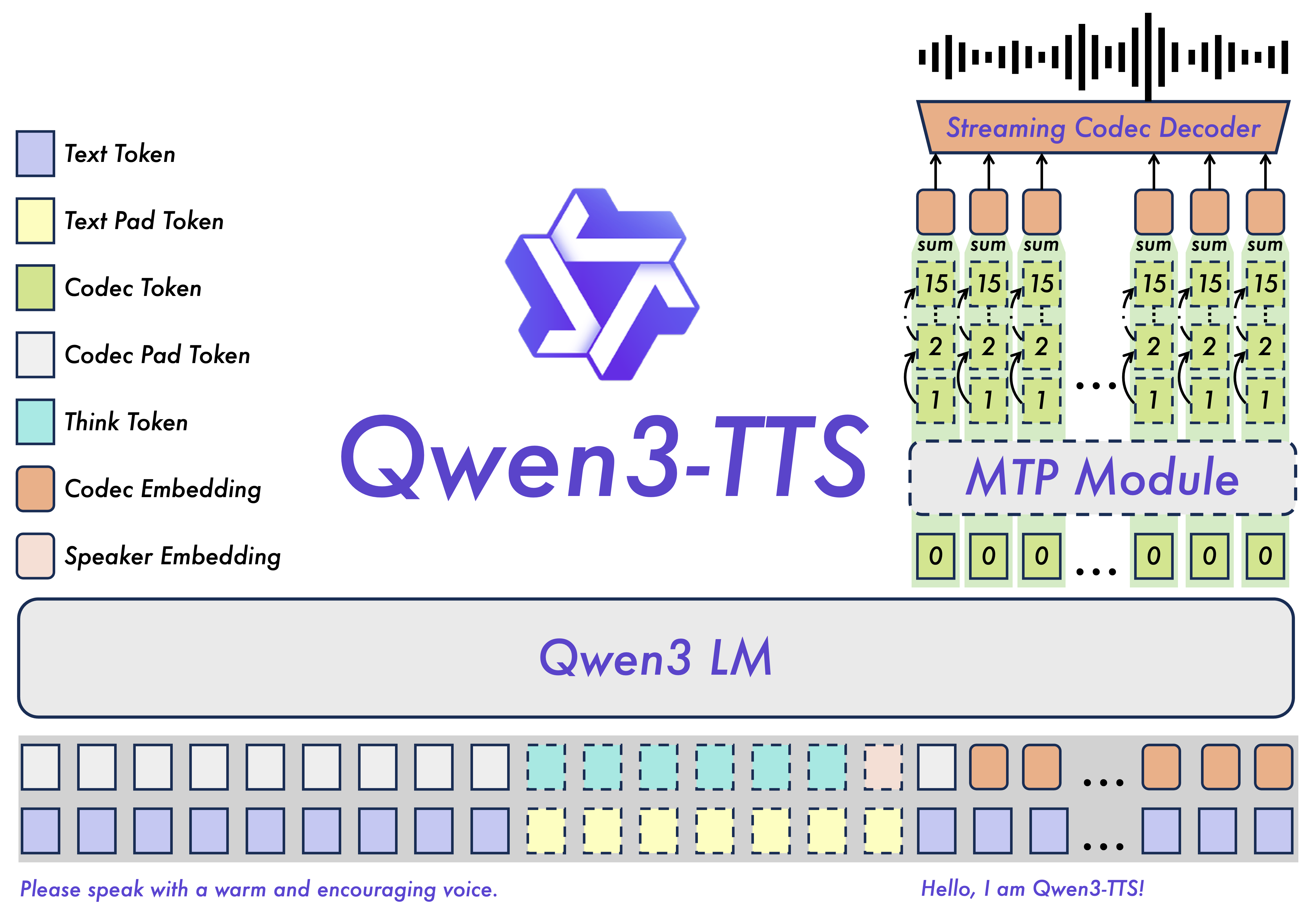
### Model Architecture
### Released Models Description and Download
Below is an introduction and download information for the Qwen3-TTS models that have already been released. Other models mentioned in the technical report will be released in the near future. Please select and download the model that fits your needs.
| Tokenizer Name | Description |
|---------------------------------|-------------|
| Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz | The Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz model which can encode the input speech into codes and decode them back into speech. |
| Model | Features | Language Support | Streaming | Instruction Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign | Performs voice design based on user-provided descriptions. | Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, French, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian | ✅ | ✅ |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice | Provides style control over target timbres via user instructions; supports 9 premium timbres covering various combinations of gender, age, language, and dialect. | Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, French, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian | ✅ | ✅ |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base | Base model capable of 3-second rapid voice clone from user audio input; can be used for fine-tuning (FT) other models. | Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, French, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian | ✅ | |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-CustomVoice | Supports 9 premium timbres covering various combinations of gender, age, language, and dialect. | Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, French, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian | ✅ | |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-Base | Base model capable of 3-second rapid voice clone from user audio input; can be used for fine-tuning (FT) other models. | Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, French, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian | ✅ | |
During model loading in the qwen-tts package or vLLM, model weights will be automatically downloaded based on the model name. However, if your runtime environment is not conducive to downloading weights during execution, you can refer to the following commands to manually download the model weights to a local directory:
```bash
# Download through ModelScope (recommended for users in Mainland China)
pip install -U modelscope
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz --local_dir ./Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice --local_dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign --local_dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base --local_dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-CustomVoice --local_dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-CustomVoice
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-Base --local_dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-Base
# Download through Hugging Face
pip install -U "huggingface_hub[cli]"
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz --local-dir ./Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice --local-dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign --local-dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base --local-dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-CustomVoice --local-dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-CustomVoice
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-Base --local-dir ./Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-Base
```
## Quickstart
### Environment Setup
The easiest way to quickly use Qwen3-TTS is to install the `qwen-tts` Python package from PyPI. This will pull in the required runtime dependencies and allow you to load any released Qwen3-TTS model. We recommend using a **fresh, isolated environment** to avoid dependency conflicts with existing packages. You can create a clean Python 3.12 environment like this:
```bash
conda create -n qwen3-tts python=3.12 -y
conda activate qwen3-tts
```
then run:
```bash
pip install -U qwen-tts
```
If you want to develop or modify the code locally, install from source in editable mode.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-TTS.git
cd Qwen3-TTS
pip install -e .
```
Additionally, we recommend using FlashAttention 2 to reduce GPU memory usage.
```bash
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
```
If your machine has less than 96GB of RAM and lots of CPU cores, run:
```bash
MAX_JOBS=4 pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
```
Also, you should have hardware that is compatible with FlashAttention 2. Read more about it in the official documentation of the [FlashAttention repository](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention). FlashAttention 2 can only be used when a model is loaded in `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`.
### Python Package Usage
After installation, you can import `Qwen3TTSModel` to run custom voice TTS, voice design, and voice clone. The model weights can be specified either as a Hugging Face model id (recommended) or as a local directory path you downloaded. For all the `generate_*` functions below, besides the parameters shown and explicitly documented, you can also pass generation kwargs supported by Hugging Face Transformers `model.generate`, e.g., `max_new_tokens`, `top_p`, etc.
#### Custom Voice Generate
For custom voice models (`Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B/0.6B-CustomVoice`), you just need to call `generate_custom_voice`, passing a single string or a batch list, along with `language`, `speaker`, and optional `instruct`. You can also call `model.get_supported_speakers()` and `model.get_supported_languages()` to see which speakers and languages the current model supports.
```python
import torch
import soundfile as sf
from qwen_tts import Qwen3TTSModel
model = Qwen3TTSModel.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice",
device_map="cuda:0",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
# single inference
wavs, sr = model.generate_custom_voice(
text="其实我真的有发现,我是一个特别善于观察别人情绪的人。",
language="Chinese", # Pass `Auto` (or omit) for auto language adaptive; if the target language is known, set it explicitly.
speaker="Vivian",
instruct="用特别愤怒的语气说", # Omit if not needed.
)
sf.write("output_custom_voice.wav", wavs[0], sr)
# batch inference
wavs, sr = model.generate_custom_voice(
text=[
"其实我真的有发现,我是一个特别善于观察别人情绪的人。",
"She said she would be here by noon."
],
language=["Chinese", "English"],
speaker=["Vivian", "Ryan"],
instruct=["", "Very happy."]
)
sf.write("output_custom_voice_1.wav", wavs[0], sr)
sf.write("output_custom_voice_2.wav", wavs[1], sr)
```
For `Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B/0.6B-CustomVoice` models, the supported speaker list and speaker descriptions are provided below. We recommend using each speaker’s native language for the best quality. Of course, each speaker can speak any language supported by the model.
| Speaker | Voice Description | Native language |
| --- | --- | --- |
| Vivian | Bright, slightly edgy young female voice. | Chinese |
| Serena | Warm, gentle young female voice. | Chinese |
| Uncle_Fu | Seasoned male voice with a low, mellow timbre. | Chinese |
| Dylan | Youthful Beijing male voice with a clear, natural timbre. | Chinese (Beijing Dialect) |
| Eric | Lively Chengdu male voice with a slightly husky brightness. | Chinese (Sichuan Dialect) |
| Ryan | Dynamic male voice with strong rhythmic drive. | English |
| Aiden | Sunny American male voice with a clear midrange. | English |
| Ono_Anna | Playful Japanese female voice with a light, nimble timbre. | Japanese |
| Sohee | Warm Korean female voice with rich emotion. | Korean |
#### Voice Design
For the voice design model (`Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign`), you can use `generate_voice_design` to provide the target text and a natural-language `instruct` description.
```python
import torch
import soundfile as sf
from qwen_tts import Qwen3TTSModel
model = Qwen3TTSModel.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign",
device_map="cuda:0",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
# single inference
wavs, sr = model.generate_voice_design(
text="哥哥,你回来啦,人家等了你好久好久了,要抱抱!",
language="Chinese",
instruct="体现撒娇稚嫩的萝莉女声,音调偏高且起伏明显,营造出黏人、做作又刻意卖萌的听觉效果。",
)
sf.write("output_voice_design.wav", wavs[0], sr)
# batch inference
wavs, sr = model.generate_voice_design(
text=[
"哥哥,你回来啦,人家等了你好久好久了,要抱抱!",
"It's in the top drawer... wait, it's empty? No way, that's impossible! I'm sure I put it there!"
],
language=["Chinese", "English"],
instruct=[
"体现撒娇稚嫩的萝莉女声,音调偏高且起伏明显,营造出黏人、做作又刻意卖萌的听觉效果。",
"Speak in an incredulous tone, but with a hint of panic beginning to creep into your voice."
]
)
sf.write("output_voice_design_1.wav", wavs[0], sr)
sf.write("output_voice_design_2.wav", wavs[1], sr)
```
#### Voice Clone
For the voice clone model (`Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B/0.6B-Base`), to clone a voice and synthesize new content, you just need to provide a reference audio clip (`ref_audio`) along with its transcript (`ref_text`). `ref_audio` can be a local file path, a URL, a base64 string, or a `(numpy_array, sample_rate)` tuple. If you set `x_vector_only_mode=True`, only the speaker embedding is used so `ref_text` is not required, but cloning quality may be reduced.
```python
import torch
import soundfile as sf
from qwen_tts import Qwen3TTSModel
model = Qwen3TTSModel.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base",
device_map="cuda:0",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
ref_audio = "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-TTS-Repo/clone.wav"
ref_text = "Okay. Yeah. I resent you. I love you. I respect you. But you know what? You blew it! And thanks to you."
wavs, sr = model.generate_voice_clone(
text="I am solving the equation: x = [-b ± √(b²-4ac)] / 2a? Nobody can — it's a disaster (◍•͈⌔•͈◍), very sad!",
language="English",
ref_audio=ref_audio,
ref_text=ref_text,
)
sf.write("output_voice_clone.wav", wavs[0], sr)
```
If you need to reuse the same reference prompt across multiple generations (to avoid recomputing prompt features), build it once with `create_voice_clone_prompt` and pass it via `voice_clone_prompt`.
```python
prompt_items = model.create_voice_clone_prompt(
ref_audio=ref_audio,
ref_text=ref_text,
x_vector_only_mode=False,
)
wavs, sr = model.generate_voice_clone(
text=["Sentence A.", "Sentence B."],
language=["English", "English"],
voice_clone_prompt=prompt_items,
)
sf.write("output_voice_clone_1.wav", wavs[0], sr)
sf.write("output_voice_clone_2.wav", wavs[1], sr)
```
For more examples of reusable voice clone prompts, batch cloning, and batch inference, please refer to the [example codes](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-TTS/blob/main/examples/test_model_12hz_base.py). With those examples and the `generate_voice_clone` function description, you can explore more advanced usage patterns.
#### Voice Design then Clone
If you want a designed voice that you can reuse like a cloned speaker, a practical workflow is: (1) use the **VoiceDesign** model to synthesize a short reference clip that matches your target persona, (2) feed that clip into `create_voice_clone_prompt` to build a reusable prompt, and then (3) call `generate_voice_clone` with `voice_clone_prompt` to generate new content without re-extracting features every time. This is especially useful when you want a consistent character voice across many lines.
```python
import torch
import soundfile as sf
from qwen_tts import Qwen3TTSModel
# create a reference audio in the target style using the VoiceDesign model
design_model = Qwen3TTSModel.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign",
device_map="cuda:0",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
ref_text = "H-hey! You dropped your... uh... calculus notebook? I mean, I think it's yours? Maybe?"
ref_instruct = "Male, 17 years old, tenor range, gaining confidence - deeper breath support now, though vowels still tighten when nervous"
ref_wavs, sr = design_model.generate_voice_design(
text=ref_text,
language="English",
instruct=ref_instruct
)
sf.write("voice_design_reference.wav", ref_wavs[0], sr)
# build a reusable clone prompt from the voice design reference
clone_model = Qwen3TTSModel.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base",
device_map="cuda:0",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
voice_clone_prompt = clone_model.create_voice_clone_prompt(
ref_audio=(ref_wavs[0], sr), # or "voice_design_reference.wav"
ref_text=ref_text,
)
sentences = [
"No problem! I actually... kinda finished those already? If you want to compare answers or something...",
"What? No! I mean yes but not like... I just think you're... your titration technique is really precise!",
]
# reuse it for multiple single calls
wavs, sr = clone_model.generate_voice_clone(
text=sentences[0],
language="English",
voice_clone_prompt=voice_clone_prompt,
)
sf.write("clone_single_1.wav", wavs[0], sr)
wavs, sr = clone_model.generate_voice_clone(
text=sentences[1],
language="English",
voice_clone_prompt=voice_clone_prompt,
)
sf.write("clone_single_2.wav", wavs[0], sr)
# or batch generate in one call
wavs, sr = clone_model.generate_voice_clone(
text=sentences,
language=["English", "English"],
voice_clone_prompt=voice_clone_prompt,
)
for i, w in enumerate(wavs):
sf.write(f"clone_batch_{i}.wav", w, sr)
```
#### Tokenizer Encode and Decode
If you only want to encode and decode audio for transport or training and so on, `Qwen3TTSTokenizer` supports encode/decode with paths, URLs, numpy waveforms, and dict/list payloads, for example:
```python
import soundfile as sf
from qwen_tts import Qwen3TTSTokenizer
tokenizer = Qwen3TTSTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz",
device_map="cuda:0",
)
enc = tokenizer.encode("https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-TTS-Repo/tokenizer_demo_1.wav")
wavs, sr = tokenizer.decode(enc)
sf.write("decode_output.wav", wavs[0], sr)
```
For more tokenizer examples (including different input formats and batch usage), please refer to the [example codes](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-TTS/blob/main/examples/test_tokenizer_12hz.py). With those examples and the description for `Qwen3TTSTokenizer`, you can explore more advanced usage patterns.
### Launch Local Web UI Demo
To launch the Qwen3-TTS web ui demo, simply install the `qwen-tts` package and run `qwen-tts-demo`. Use the command below for help:
```bash
qwen-tts-demo --help
```
To launch the demo, you can use the following commands:
```bash
# CustomVoice model
qwen-tts-demo Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice --ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
# VoiceDesign model
qwen-tts-demo Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign --ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
# Base model
qwen-tts-demo Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base --ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
```
And then open `http://:8000`, or access it via port forwarding in tools like VS Code.
#### Base Model HTTPS Notes
To avoid browser microphone permission issues after deploying the server, for Base model deployments, it is recommended/required to run the gradio service over **HTTPS** (especially when accessed remotely or behind modern browsers/gateways). Use `--ssl-certfile` and `--ssl-keyfile` to enable HTTPS. First we need to generate a private key and a self-signed cert (valid for 365 days):
```bash
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 \
-keyout key.pem -out cert.pem \
-days 365 -nodes \
-subj "/CN=localhost"
```
Then run the demo with HTTPS:
```bash
qwen-tts-demo Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base \
--ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8000 \
--ssl-certfile cert.pem \
--ssl-keyfile key.pem \
--no-ssl-verify
```
And open `https://:8000` to experience it. If your browser shows a warning, it’s expected for self-signed certificates. For production, use a real certificate.
### DashScope API Usage
To further explore Qwen3-TTS, we encourage you to try our DashScope API for a faster and more efficient experience. For detailed API information and documentation, please refer to the following:
| API Description | API Documentation (Mainland China) | API Documentation (International) |
|------------------|-----------------------------------|------------------------------------|
| Real-time API for Qwen3-TTS of custom voice model. | [https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-tts-realtime](https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-tts-realtime) | [https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-tts-realtime](https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-tts-realtime) |
| Real-time API for Qwen3-TTS of voice clone model. | [https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-cloning](https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-cloning) | [https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-cloning](https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-cloning) |
| Real-time API for Qwen3-TTS of voice design model. | [https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-design](https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-design) | [https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-design](https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-tts-voice-design) |
## vLLM Usage
vLLM officially provides day-0 support for Qwen3-TTS! Welcome to use vLLM-Omni for Qwen3-TTS deployment and inference. For installation and more details, please check [vLLM-Omni official documentation](https://docs.vllm.ai/projects/vllm-omni/en/latest/getting_started/quickstart/#installation). Now only offline inference is supported. Online serving will be supported later, and vLLM-Omni will continue to offer support and optimization for Qwen3-TTS in areas such as inference speed and streaming capabilities.
### Offline Inference
You can use vLLM-Omni to inference Qwen3-TTS locally, we provide examples in [vLLM-Omni repo](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm-omni/tree/main/examples/offline_inference/qwen3_tts) which can generate audio output:
```bash
# git clone https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm-omni.git
# cd vllm-omni/examples/offline_inference/qwen3_tts
# Run a single sample with CustomVoice task
python end2end.py --query-type CustomVoice
# Batch sample (multiple prompts in one run) with CustomVoice task:
python end2end.py --query-type CustomVoice --use-batch-sample
# Run a single sample with VoiceDesign task
python end2end.py --query-type VoiceDesign
# Batch sample (multiple prompts in one run) with VoiceDesign task:
python end2end.py --query-type VoiceDesign --use-batch-sample
# Run a single sample with Base task in icl mode-tag
python end2end.py --query-type Base --mode-tag icl
```
## Fine Tuning
Please refer to [Qwen3-TTS-Finetuning](finetuning/) for detailed instructions on fine-tuning Qwen3-TTS.
## Evaluation
During evaluation, we ran inference for all models with `dtype=torch.bfloat16` and set `max_new_tokens=2048`. All other sampling parameters used the defaults from the checkpoint’s `generate_config.json`. For the Seed-Test and InstructTTS-Eval test sets, we set `language="auto"`, while for all other test sets we explicitly passed the corresponding `language`. The detailed results are shown below.
Speech Generation Benchmarks
*Zero-shot speech generation on the Seed-TTS test set. Performance is measured by Word Error Rate (WER, ↓), where lower is better.*
| Datasets |
Model |
Performance |
| Content Consistency |
SEED
test-zh | test-en |
Seed-TTS (Anastassiou et al., 2024) |
1.12 |
2.25 |
| MaskGCT (Wang et al., 2024) |
2.27 |
2.62 |
| E2 TTS (Eskimez et al., 2024) |
1.97 |
2.19 |
| F5-TTS (Chen et al., 2024) |
1.56 |
1.83 |
| Spark TTS (Wang et al., 2025) |
1.20 |
1.98 |
| Llasa-8B (Ye et al., 2025b) |
1.59 |
2.97 |
| KALL-E (Xia et al., 2024) |
0.96 |
1.94 |
| FireRedTTS 2 (Xie et al., 2025) |
1.14 |
1.95 |
| CosyVoice 3 (Du et al., 2025) |
0.71 |
1.45 |
| MiniMax-Speech (Zhang et al., 2025a) |
0.83 |
1.65 |
| Qwen3-TTS-25Hz-0.6B-Base |
1.18 |
1.64 |
| Qwen3-TTS-25Hz-1.7B-Base |
1.10 |
1.49 |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-Base |
0.92 |
1.32 |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base |
0.77 |
1.24 |
*Multilingual speech generation on the TTS multilingual test set. Performance is measured by Word Error Rate (WER, ↓) for content consistency and Cosine Similarity (SIM, ↑) for speaker similarity.*
| Language |
Qwen3-TTS-25Hz |
Qwen3-TTS-12Hz |
MiniMax |
ElevenLabs |
| 0.6B-Base |
1.7B-Base |
0.6B-Base |
1.7B-Base |
| Content Consistency |
| Chinese |
1.108 |
0.777 |
1.145 |
0.928 |
2.252 |
16.026 |
| English |
1.048 |
1.014 |
0.836 |
0.934 |
2.164 |
2.339 |
| German |
1.501 |
0.960 |
1.089 |
1.235 |
1.906 |
0.572 |
| Italian |
1.169 |
1.105 |
1.534 |
0.948 |
1.543 |
1.743 |
| Portuguese |
2.046 |
1.778 |
2.254 |
1.526 |
1.877 |
1.331 |
| Spanish |
2.031 |
1.491 |
1.491 |
1.126 |
1.029 |
1.084 |
| Japanese |
4.189 |
5.121 |
6.404 |
3.823 |
3.519 |
10.646 |
| Korean |
2.852 |
2.631 |
1.741 |
1.755 |
1.747 |
1.865 |
| French |
2.852 |
2.631 |
2.931 |
2.858 |
4.099 |
5.216 |
| Russian |
5.957 |
4.535 |
4.458 |
3.212 |
4.281 |
3.878 |
| Speaker Similarity |
| Chinese |
0.797 |
0.796 |
0.811 |
0.799 |
0.780 |
0.677 |
| English |
0.811 |
0.815 |
0.829 |
0.775 |
0.756 |
0.613 |
| German |
0.749 |
0.737 |
0.769 |
0.775 |
0.733 |
0.614 |
| Italian |
0.722 |
0.718 |
0.792 |
0.817 |
0.699 |
0.579 |
| Portuguese |
0.790 |
0.783 |
0.794 |
0.817 |
0.805 |
0.711 |
| Spanish |
0.732 |
0.731 |
0.812 |
0.814 |
0.762 |
0.615 |
| Japanese |
0.810 |
0.807 |
0.798 |
0.788 |
0.776 |
0.738 |
| Korean |
0.824 |
0.814 |
0.812 |
0.799 |
0.779 |
0.700 |
| French |
0.698 |
0.703 |
0.700 |
0.714 |
0.628 |
0.535 |
| Russian |
0.734 |
0.744 |
0.781 |
0.792 |
0.761 |
0.676 |
*Cross-lingual speech generation on the Cross-Lingual benchmark. Performance is measured by Mixed Error Rate (WER for English, CER for others, ↓).*
| Task |
Qwen3-TTS-25Hz-1.7B-Base |
Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base |
CosyVoice3 |
CosyVoice2 |
| en-to-zh |
5.66 |
4.77 |
5.09 |
13.5 |
| ja-to-zh |
3.92 |
3.43 |
3.05 |
48.1 |
| ko-to-zh |
1.14 |
1.08 |
1.06 |
7.70 |
| zh-to-en |
2.91 |
2.77 |
2.98 |
6.47 |
| ja-to-en |
3.95 |
3.04 |
4.20 |
17.1 |
| ko-to-en |
3.48 |
3.09 |
4.19 |
11.2 |
| zh-to-ja |
9.29 |
8.40 |
7.08 |
13.1 |
| en-to-ja |
7.74 |
7.21 |
6.80 |
14.9 |
| ko-to-ja |
4.17 |
3.67 |
3.93 |
5.86 |
| zh-to-ko |
8.12 |
4.82 |
14.4 |
24.8 |
| en-to-ko |
6.83 |
5.14 |
5.87 |
21.9 |
| ja-to-ko |
6.86 |
5.59 |
7.92 |
21.5 |
*Controllable speech generation on InstructTTSEval. Performance is measured by Attribute Perception and Synthesis accuracy (APS), Description-Speech Consistency (DSD), and Response Precision (RP).*
| Type |
Model |
InstructTTSEval-ZH |
InstructTTSEval-EN |
| APS (↑) |
DSD (↑) |
RP (↑) |
APS (↑) |
DSD (↑) |
RP (↑) |
Target
Speaker |
Gemini-flash |
88.2 |
90.9 |
77.3 |
92.3 |
93.8 |
80.1 |
| Gemini-pro |
89.0 |
90.1 |
75.5 |
87.6 |
86.0 |
67.2 |
| Qwen3TTS-25Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice |
83.1 |
75.0 |
63.0 |
79.0 |
82.8 |
69.3 |
| Qwen3TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice |
83.0 |
77.8 |
61.2 |
77.3 |
77.1 |
63.7 |
| GPT-4o-mini-tts |
54.9 |
52.3 |
46.0 |
76.4 |
74.3 |
54.8 |
Voice
Design |
Qwen3TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VD |
85.2 |
81.1 |
65.1 |
82.9 |
82.4 |
68.4 |
| Mimo-Audio-7B-Instruct (Zhang et al., 2025b) |
75.7 |
74.3 |
61.5 |
80.6 |
77.6 |
59.5 |
| VoiceSculptor (Hu et al., 2026) |
75.7 |
64.7 |
61.5 |
- |
- |
- |
| Hume |
- |
- |
- |
83.0 |
75.3 |
54.3 |
| VoxInstruct (Zhou et al., 2024) |
47.5 |
52.3 |
42.6 |
54.9 |
57.0 |
39.3 |
| Parler-tts-mini (Lyth & King, 2024) |
- |
- |
- |
63.4 |
48.7 |
28.6 |
| Parler-tts-large (Lyth & King, 2024) |
- |
- |
- |
60.0 |
45.9 |
31.2 |
| PromptTTS (Guo et al., 2023) |
- |
- |
- |
64.3 |
47.2 |
31.4 |
| PromptStyle (Liu et al., 2023) |
- |
- |
- |
57.4 |
46.4 |
30.9 |
*Target-Speaker Multilingual Speech Generation on the TTS multilingual test set. Performance is measured by Word Error Rate (WER, ↓).*
| Language |
Qwen3-TTS-25Hz |
Qwen3-TTS-12Hz |
GPT-4o-Audio
Preview |
| 0.6B-CustomVoice |
1.7B-CustomVoice |
0.6B-CustomVoice |
1.7B-CustomVoice |
| Chinese |
0.874 |
0.708 |
0.944 |
0.903 |
3.519 |
| English |
1.332 |
0.936 |
1.188 |
0.899 |
2.197 |
| German |
0.990 |
0.634 |
2.722 |
1.057 |
1.161 |
| Italian |
1.861 |
1.271 |
2.545 |
1.362 |
1.194 |
| Portuguese |
1.728 |
1.854 |
3.219 |
2.681 |
1.504 |
| Spanish |
1.309 |
1.284 |
1.154 |
1.330 |
4.000 |
| Japanese |
3.875 |
4.518 |
6.877 |
4.924 |
5.001 |
| Korean |
2.202 |
2.274 |
3.053 |
1.741 |
2.763 |
| French |
3.865 |
3.080 |
3.841 |
3.781 |
3.605 |
| Russian |
6.529 |
4.444 |
5.809 |
4.734 |
5.250 |
*Long speech generation results. Performance is measured by Word Error Rate (WER, ↓).*
| Datasets |
Model |
Performance |
| Content Consistency |
| long-zh | long-en |
Higgs-Audio-v2 (chunk) (Boson AI, 2025) |
5.505 |
6.917 |
| VibeVoice (Peng et al., 2025) |
22.619 |
1.780 |
| VoxCPM (Zhou et al., 2025) |
4.835 |
7.474 |
| Qwen3-TTS-25Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice |
1.517 |
1.225 |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice |
2.356 |
2.812 |
Speech Tokenizer Benchmarks
*Comparison between different supervised semantic speech tokenizers on ASR Task.*
| Model |
Codebook Size |
FPS |
C.V. EN |
C.V. CN |
Fluers EN |
Fluers CN |
| S3 Tokenizer(VQ) (Du et al., 2024a) |
4096 |
50 |
12.06 |
15.38 |
- |
- |
| S3 Tokenizer(VQ) (Du et al., 2024a) |
4096 |
25 |
11.56 |
18.26 |
7.65 |
5.03 |
| S3 Tokenizer(FSQ) (Du et al., 2024a) |
6561 |
25 |
10.67 |
7.29 |
6.58 |
4.43 |
| Qwen-TTS-Tokenizer-25Hz (Stage 1) |
32768 |
25 |
7.51 |
10.73 |
3.07 |
4.23 |
| Qwen-TTS-Tokenizer-25Hz (Stage 2) |
32768 |
25 |
10.40 |
14.99 |
4.14 |
4.67 |
*Comparison between different semantic-related speech tokenizers.*
| Model |
NQ |
Codebook Size |
FPS |
PESQ_WB |
PESQ_NB |
STOI |
UTMOS |
SIM |
| SpeechTokenizer (Zhang et al., 2023a) |
8 |
1024 |
50 |
2.60 |
3.05 |
0.92 |
3.90 |
0.85 |
| X-codec (Ye et al., 2025a) |
2 |
1024 |
50 |
2.68 |
3.27 |
0.86 |
4.11 |
0.84 |
| X-codec 2 (Ye et al., 2025b) |
1 |
65536 |
50 |
2.43 |
3.04 |
0.92 |
4.13 |
0.82 |
| XY-Tokenizer (Gong et al., 2025) |
8 |
1024 |
12.5 |
2.41 |
3.00 |
0.91 |
3.98 |
0.83 |
| Mimi (Défossez et al., 2024) |
16 |
2048 |
12.5 |
2.88 |
3.42 |
0.94 |
3.87 |
0.87 |
| FireredTTS 2 Tokenizer (Xie et al., 2025) |
16 |
2048 |
12.5 |
2.73 |
3.28 |
0.94 |
3.88 |
0.87 |
| Qwen-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz |
16 |
2048 |
12.5 |
3.21 |
3.68 |
0.96 |
4.16 |
0.95 |
## Citation
If you find our paper and code useful in your research, please consider giving a star :star: and citation :pencil: :)
```BibTeX
@article{Qwen3-TTS,
title={Qwen3-TTS Technical Report},
author={Hangrui Hu and Xinfa Zhu and Ting He and Dake Guo and Bin Zhang and Xiong Wang and Zhifang Guo and Ziyue Jiang and Hongkun Hao and Zishan Guo and Xinyu Zhang and Pei Zhang and Baosong Yang and Jin Xu and Jingren Zhou and Junyang Lin},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2601.15621},
year={2026}
}
```



