

🤗 Hugging Face | 🤖 ModelScope | 📑 Blog | 📑 Paper
🖥️ Hugging Face Demo | 🖥️ ModelScope Demo | 💬 WeChat (微信) | 🫨 Discord | 📑 API
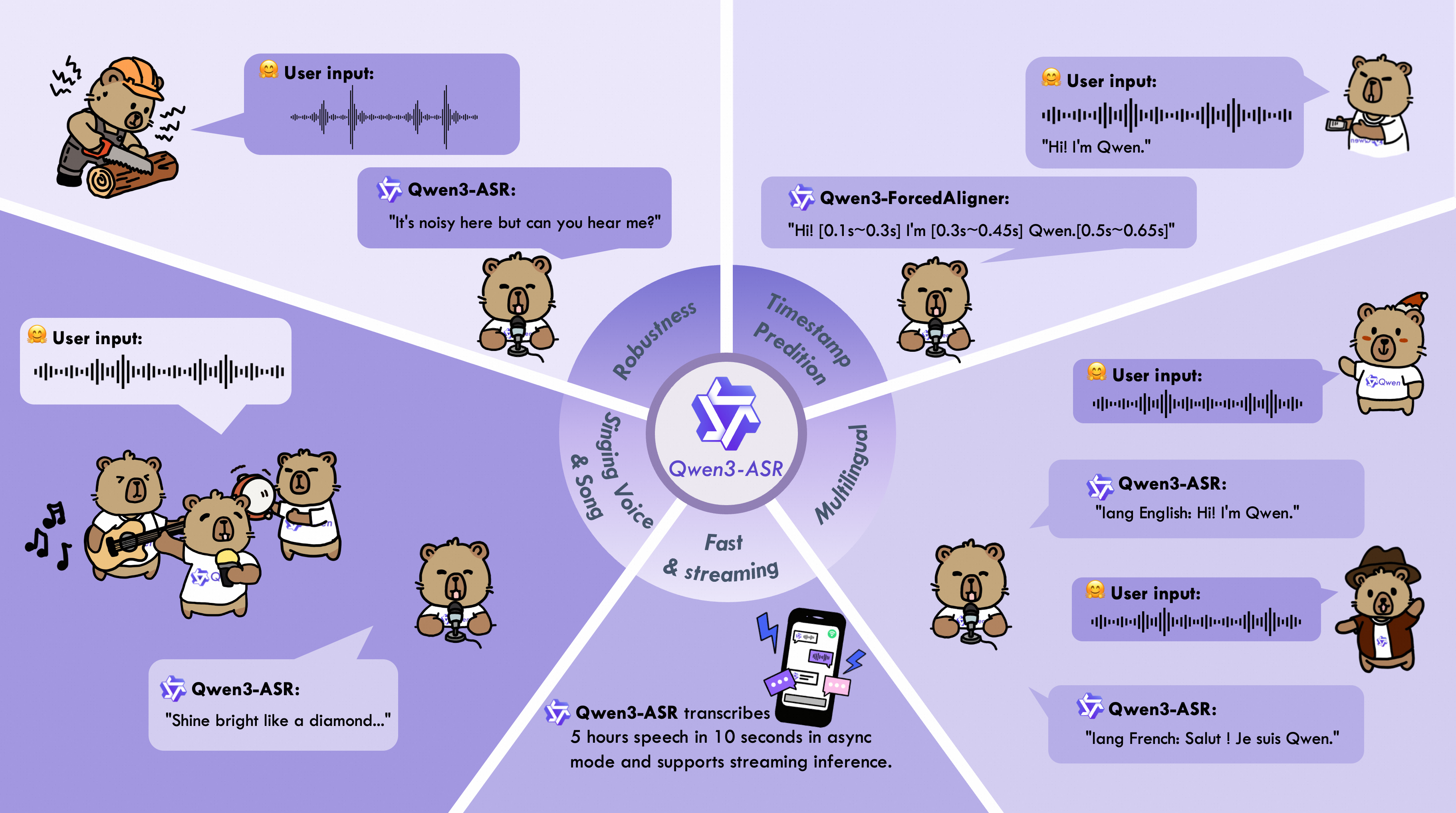
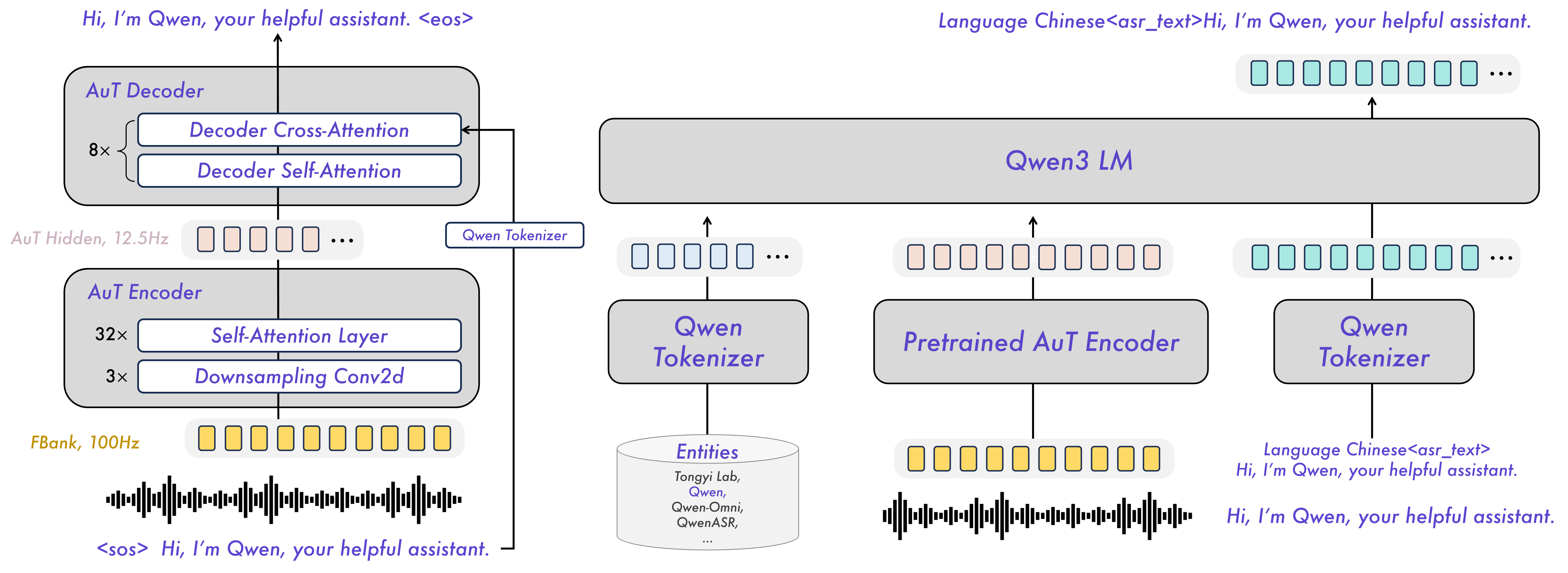
The Qwen3-ASR family includes Qwen3-ASR-1.7B and Qwen3-ASR-0.6B, which support language identification and ASR for 52 languages and dialects. Both leverage large-scale speech training data and the strong audio understanding capability of their foundation model, Qwen3-Omni. Experiments show that the 1.7B version achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source ASR models and is competitive with the strongest proprietary commercial APIs. Here are the main features: * **All-in-one**: Qwen3-ASR-1.7B and Qwen3-ASR-0.6B support language identification and speech recognition for 30 languages and 22 Chinese dialects, so as to English accents from multiple countries and regions. * **Excellent and Fast**: The Qwen3-ASR family ASR models maintains high-quality and robust recognition under complex acoustic environments and challenging text patterns. Qwen3-ASR-1.7B achieves strong performance on both open-sourced and internal benchmarks. While the 0.6B version achieves accuracy-efficient trade-off, it reaches 2000 times throughput at a concurrency of 128. They both achieve streaming / offline unified inference with single model and support transcribe long audio. * **Novel and strong forced alignment Solution**: We introduce Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B, which supports timestamp prediction for arbitrary units within up to 5 minutes of speech in 11 languages. Evaluations show its timestamp accuracy surpasses E2E based forced-alignment models. * **Comprehensive inference toolkit**: In addition to open-sourcing the architectures and weights of the Qwen3-ASR series, we also release a powerful, full-featured inference framework that supports vLLM-based batch inference, asynchronous serving, streaming inference, timestamp prediction, and more. ### Model Architecture
### Released Models Description and Download
Below is an introduction and download information for the Qwen3-ASR models. Please select and download the model that fits your needs.
| Model | Supported Languages | Supported Dialects | Inference Mode | Audio Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-ASR-1.7B & Qwen3-ASR-0.6B | Chinese (zh), English (en), Cantonese (yue), Arabic (ar), German (de), French (fr), Spanish (es), Portuguese (pt), Indonesian (id), Italian (it), Korean (ko), Russian (ru), Thai (th), Vietnamese (vi), Japanese (ja), Turkish (tr), Hindi (hi), Malay (ms), Dutch (nl), Swedish (sv), Danish (da), Finnish (fi), Polish (pl), Czech (cs), Filipino (fil), Persian (fa), Greek (el), Hungarian (hu), Macedonian (mk), Romanian (ro) | Anhui, Dongbei, Fujian, Gansu, Guizhou, Hebei, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Ningxia, Shandong, Shaanxi, Shanxi, Sichuan, Tianjin, Yunnan, Zhejiang, Cantonese (Hong Kong accent), Cantonese (Guangdong accent), Wu language, Minnan language. | Offline / Streaming | Speech, Singing Voice, Songs with BGM |
| Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B | Chinese, English, Cantonese, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish | -- | NAR | Speech |
During model loading in the `qwen-asr` package or vLLM, model weights will be downloaded automatically based on the model name. However, if your runtime environment does not allow downloading weights during execution, you can use the following commands to manually download the model weights to a local directory:
```bash
# Download through ModelScope (recommended for users in Mainland China)
pip install -U modelscope
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B --local_dir ./Qwen3-ASR-1.7B
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-0.6B --local_dir ./Qwen3-ASR-0.6B
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B --local_dir ./Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B
# Download through Hugging Face
pip install -U "huggingface_hub[cli]"
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B --local-dir ./Qwen3-ASR-1.7B
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-0.6B --local-dir ./Qwen3-ASR-0.6B
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B --local-dir ./Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B
```
## Quickstart
### Environment Setup
The easiest way to use Qwen3-ASR is to install the `qwen-asr` Python package from PyPI. This will pull in the required runtime dependencies and allow you to load any released Qwen3-ASR model. If you’d like to simplify environment setup further, you can also use our official [Docker image](#docker). The `qwen-asr` package provides two backends: the transformers backend and the vLLM backend. For usage instructions for different backends, please refer to [Python Package Usage](#python-package-usage). We recommend using a **fresh, isolated environment** to avoid dependency conflicts with existing packages. You can create a clean Python 3.12 environment like this:
```bash
conda create -n qwen3-asr python=3.12 -y
conda activate qwen3-asr
```
Run the following command to get the minimal installation with transformers-backend support:
```bash
pip install -U qwen-asr
```
To enable the vLLM backend for faster inference and streaming support, run:
```bash
pip install -U qwen-asr[vllm]
```
If you want to develop or modify the code locally, install from source in editable mode:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-ASR.git
cd Qwen3-ASR
pip install -e .
# support vLLM backend
# pip install -e ".[vllm]"
```
Additionally, we recommend using FlashAttention 2 to reduce GPU memory usage and accelerate inference speed, especially for long inputs and large batch sizes.
```bash
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
```
If your machine has less than 96GB of RAM and lots of CPU cores, run:
```bash
MAX_JOBS=4 pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
```
Also, you should have hardware that is compatible with FlashAttention 2. Read more about it in the official documentation of the [FlashAttention repository](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention). FlashAttention 2 can only be used when a model is loaded in `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`.
### Python Package Usage
#### Quick Inference
The `qwen-asr` package provides two backends: **transformers backend** and **vLLM backend**. You can pass audio inputs as a local path, a URL, base64 data, or a `(np.ndarray, sr)` tuple, and run batch inference. To quickly try Qwen3-ASR, you can use `Qwen3ASRModel.from_pretrained(...)` for the transformers backend with the following code:
```python
import torch
from qwen_asr import Qwen3ASRModel
model = Qwen3ASRModel.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="cuda:0",
# attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
max_inference_batch_size=32, # Batch size limit for inference. -1 means unlimited. Smaller values can help avoid OOM.
max_new_tokens=256, # Maximum number of tokens to generate. Set a larger value for long audio input.
)
results = model.transcribe(
audio="https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-ASR-Repo/asr_en.wav",
language=None, # set "English" to force the language
)
print(results[0].language)
print(results[0].text)
```
If you want to return timestamps, pass `forced_aligner` and its init kwargs. Here is an example of batch inference with timestamps output:
```python
import torch
from qwen_asr import Qwen3ASRModel
model = Qwen3ASRModel.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="cuda:0",
# attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
max_inference_batch_size=32, # Batch size limit for inference. -1 means unlimited. Smaller values can help avoid OOM.
max_new_tokens=256, # Maximum number of tokens to generate. Set a larger value for long audio input.
forced_aligner="Qwen/Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B",
forced_aligner_kwargs=dict(
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="cuda:0",
# attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
),
)
results = model.transcribe(
audio=[
"https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-ASR-Repo/asr_zh.wav",
"https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-ASR-Repo/asr_en.wav",
],
language=["Chinese", "English"], # can also be set to None for automatic language detection
return_time_stamps=True,
)
for r in results:
print(r.language, r.text, r.time_stamps[0])
```
For more detailed usage examples, please refer to the [example code](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-ASR/blob/main/examples/example_qwen3_asr_transformers.py) for the transformers backend.
#### vLLM Backend
If you want the fastest inference speed with Qwen3-ASR, we strongly recommend using the vLLM backend by initializing the model with `Qwen3ASRModel.LLM(...)`. Example code is provided below. Note that you must install it via `pip install -U qwen-asr[vllm]`. If you want the model to output timestamps, it’s best to install FlashAttention via `pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation` to speed up inference for the forced aligner model. Remember to wrap your code under `if __name__ == '__main__':` to avoid the `spawn` error described in [vLLM Troubleshooting](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/usage/troubleshooting/#python-multiprocessing).
```python
import torch
from qwen_asr import Qwen3ASRModel
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = Qwen3ASRModel.LLM(
model="Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B",
gpu_memory_utilization=0.7,
max_inference_batch_size=128, # Batch size limit for inference. -1 means unlimited. Smaller values can help avoid OOM.
max_new_tokens=4096, # Maximum number of tokens to generate. Set a larger value for long audio input.
forced_aligner="Qwen/Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B",
forced_aligner_kwargs=dict(
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="cuda:0",
# attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
),
)
results = model.transcribe(
audio=[
"https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-ASR-Repo/asr_zh.wav",
"https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-ASR-Repo/asr_en.wav",
],
language=["Chinese", "English"], # can also be set to None for automatic language detection
return_time_stamps=True,
)
for r in results:
print(r.language, r.text, r.time_stamps[0])
```
For more detailed usage examples, please refer to the [example code](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-ASR/blob/main/examples/example_qwen3_asr_vllm.py) for the vLLM backend. In addition, you can start a vLLM server via the `qwen-asr-serve` command, which is a wrapper around `vllm serve`. You can pass any arguments supported by `vllm serve`, for example:
```bash
qwen-asr-serve Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B --gpu-memory-utilization 0.8 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
```
And send requests to the server via:
```python
import requests
url = "http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions"
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
data = {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "audio_url",
"audio_url": {
"url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-ASR-Repo/asr_en.wav"
},
}
],
}
]
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data, timeout=300)
response.raise_for_status()
content = response.json()['choices'][0]['message']['content']
print(content)
# parse ASR output if you want
from qwen_asr import parse_asr_output
language, text = parse_asr_output(content)
print(language)
print(text)
```
#### Streaming Inference
Qwen3-ASR fully supports streaming inference. Currently, streaming inference is only available with the vLLM backend. Note that streaming inference does not support batch inference or returning timestamps. Please refer to the [example code](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-ASR/blob/main/examples/example_qwen3_asr_vllm_streaming.py) for details. You can also launch a streaming web demo through the [guide](#streaming-demo) to experience Qwen3-ASR’s streaming transcription capabilities.
#### ForcedAligner Usage
`Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B` can align text–speech pairs and return word or character level timestamps. Here is an example of using the forced aligner directly:
```python
import torch
from qwen_asr import Qwen3ForcedAligner
model = Qwen3ForcedAligner.from_pretrained(
"Qwen/Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="cuda:0",
# attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
)
results = model.align(
audio="https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen3-ASR-Repo/asr_zh.wav",
text="甚至出现交易几乎停滞的情况。",
language="Chinese",
)
print(results[0])
print(results[0][0].text, results[0][0].start_time, results[0][0].end_time)
```
In addition, the forced aligner supports local paths / URLs / base64 data / `(np.ndarray, sr)` inputs and batch inference. Please refer to the [example code](https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3-ASR/blob/main/examples/example_qwen3_forced_aligner.py) for details.
### DashScope API Usage
To further explore Qwen3-ASR, we encourage you to try our DashScope API for a faster and more efficient experience. For detailed API information and documentation, please refer to the following:
| API Description | API Documentation (Mainland China) | API Documentation (International) |
|------------------|-----------------------------------|------------------------------------|
| Real-time API for Qwen3-ASR. | [https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-real-time-speech-recognition](https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-real-time-speech-recognition) | [https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-real-time-speech-recognition](https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-real-time-speech-recognition) |
| FileTrans API for Qwen3-ASR. | [https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-speech-recognition](https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/qwen-speech-recognition) | [https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-speech-recognition](https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/model-studio/qwen-speech-recognition) |
## Launch Local Web UI Demo
### Gradio Demo
To launch the Qwen3-ASR web UI gradio demo, install the `qwen-asr` package and run `qwen-asr-demo`. Use the command below for help:
```bash
qwen-asr-demo --help
```
To launch the demo, you can use the following commands:
```bash
# Transformers backend
qwen-asr-demo \
--asr-checkpoint Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B \
--backend transformers \
--cuda-visible-devices 0 \
--ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
# Transformers backend + Forced Aligner (enable timestamps)
qwen-asr-demo \
--asr-checkpoint Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B \
--aligner-checkpoint Qwen/Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B \
--backend transformers \
--cuda-visible-devices 0 \
--backend-kwargs '{"device_map":"cuda:0","dtype":"bfloat16","max_inference_batch_size":8,"max_new_tokens":256}' \
--aligner-kwargs '{"device_map":"cuda:0","dtype":"bfloat16"}' \
--ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
# vLLM backend + Forced Aligner (enable timestamps)
qwen-asr-demo \
--asr-checkpoint Qwen/Qwen3-ASR-1.7B \
--aligner-checkpoint Qwen/Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B \
--backend vllm \
--cuda-visible-devices 0 \
--backend-kwargs '{"gpu_memory_utilization":0.7,"max_inference_batch_size":8,"max_new_tokens":2048}' \
--aligner-kwargs '{"device_map":"cuda:0","dtype":"bfloat16"}' \
--ip 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
```
Then open `http:// Dialect coverage: Results for Dialog-Accented English are averaged over 16 accents, and results for Dialog-Chinese Dialects are averaged over 22 Chinese dialects. Language coverage: MLS includes 8 languages: {da, de, en, es, fr, it, pl, pt}. Language coverage: The language sets follow Multilingual ASR Benchmarks. Here, Fleurs corresponds to Fleurs†† in Multilingual ASR Benchmarks and covers 30 languages.ASR Benchmarks on Public Datasets (WER ↓)
GPT-4o
-TranscribeGemini-2.5
-ProDoubao-ASR
Whisper
-large-v3Fun-ASR
-MLT-NanoQwen3-ASR
-0.6BQwen3-ASR
-1.7B
English (en)
Librispeech
clean | other1.39 | 3.75
2.89 | 3.56
2.78 | 5.70
1.51 | 3.97
1.68 | 4.03
2.11 | 4.55
1.63 | 3.38
GigaSpeech
25.50
9.37
9.55
9.76
-
8.88
8.45
CV-en
9.08
14.49
13.78
9.90
9.90
9.92
7.39
Fleurs-en
2.40
2.94
6.31
4.08
5.49
4.39
3.35
MLS-en
5.12
3.68
7.09
4.87
-
6.00
4.58
Tedlium
7.69
6.15
4.91
6.84
-
3.85
4.50
VoxPopuli
10.29
11.36
12.12
12.05
-
9.96
9.15
Chinese (zh)
WenetSpeech
net | meeting15.30 | 32.27
14.43 | 13.47
N/A
9.86 | 19.11
6.35 | -
5.97 | 6.88
4.97 | 5.88
AISHELL-2-test
4.24
11.62
2.85
5.06
-
3.15
2.71
SpeechIO
12.86
5.30
2.93
7.56
-
3.44
2.88
Fleurs-zh
2.44
2.71
2.69
4.09
3.51
2.88
2.41
CV-zh
6.32
7.70
5.95
12.91
6.20
6.89
5.35
Chinese Dialect
KeSpeech
26.87
24.71
5.27
28.79
-
7.08
5.10
Fleurs-yue
4.98
9.43
4.98
9.18
-
5.79
3.98
CV-yue
11.36
18.76
13.20
16.23
-
9.50
7.57
CV-zh-tw
6.32
7.31
4.06
7.84
-
5.59
3.77
WenetSpeech-Yue
short | long15.62 | 25.29
25.19 | 11.23
9.74 | 11.40
32.26 | 46.64
- | -
7.54 | 9.92
5.82 | 8.85
WenetSpeech-Chuan
easy | hard34.81 | 53.98
43.79 | 67.30
11.40 | 20.20
14.35 | 26.80
- | -
13.92 | 24.45
11.99 | 21.63
ASR Benchmarks on Internal Datasets (WER ↓)
GPT-4o
-TranscribeGemini-2.5
-ProDoubao-ASR
Whisper
-large-v3Fun-ASR
-MLT-NanoQwen3-ASR
-0.6BQwen3-ASR
-1.7B
Accented English
Dialog-Accented English
28.56
23.85
20.41
21.30
19.96
16.62
16.07
Chinese Mandarin
Elders&Kids
14.27
36.93
4.17
10.61
4.54
4.48
3.81
ExtremeNoise
36.11
29.06
17.04
63.17
36.55
17.88
16.17
TongueTwister
20.87
4.97
3.47
16.63
9.02
4.06
2.44
Dialog-Mandarin
20.73
12.50
6.61
14.01
7.32
7.06
6.54
Chinese Dialect
Dialog-Cantonese
16.05
14.98
7.56
31.04
5.85
4.80
4.12
Dialog-Chinese Dialects
45.37
47.70
19.85
44.55
19.41
18.24
15.94
Multilingual ASR Benchmarks (WER ↓)
GLM-ASR
-Nano-2512Whisper
-large-v3Fun-ASR
-MLT-NanoQwen3-ASR
-0.6BQwen3-ASR
-1.7B
Open-sourced Benchmarks
MLS
13.32
8.62
28.70
13.19
8.55
CommonVoice
19.40
10.77
17.25
12.75
9.18
MLC-SLM
34.93
15.68
29.94
15.84
12.74
Fleurs
16.08
5.27
10.03
7.57
4.90
Fleurs†
20.05
6.85
31.89
10.37
6.62
Fleurs††
24.83
8.16
47.84
21.80
12.60
Qwen-ASR Internal Benchmarks
News-Multilingual
49.40
14.80
65.07
17.39
12.80
CommonVoice includes 13 languages: {en, zh, yue, zh_TW, ar, de, es, fr, it, ja, ko, pt, ru}.
MLC-SLM includes 11 languages: {en, fr, de, it, pt, es, ja, ko, ru, th, vi}.
Fleurs includes 12 languages: {en, zh, yue, ar, de, es, fr, it, ja, ko, pt, ru }.
Fleurs† includes 8 additional languages beyond Fleurs: {hi, id, ms, nl, pl, th, tr, vi}.
Fleurs†† includes 10 additional languages beyond Fleurs†: {cs, da, el, fa, fi, fil, hu, mk, ro, sv}.
News-Multilingual includes 15 languages: {ar, de, es, fr, hi, id, it, ja, ko, nl, pl, pt, ru, th, vi}.Language Identification Accuracy (%) ↑
Whisper-large-v3
Qwen3-ASR-0.6B
Qwen3-ASR-1.7B
MLS
99.9
99.3
99.9
CommonVoice
92.7
98.2
98.7
MLC-SLM
89.2
92.7
94.1
Fleurs
94.6
97.1
98.7
Avg.
94.1
96.8
97.9
Singing Voice & Song Transcription (WER ↓)
GPT-4o
-TranscribeGemini-2.5
-ProDoubao-ASR
-1.0Whisper
-large-v3Fun-ASR-MLT
-NanoQwen3-ASR
-1.7B
Singing
M4Singer
16.77
20.88
7.88
13.58
7.29
5.98
MIR-1k-vocal
11.87
9.85
6.56
11.71
8.17
6.25
Opencpop
7.93
6.49
3.80
9.52
2.98
3.08
Popcs
32.84
15.13
8.97
13.77
9.42
8.52
Songs with BGM
EntireSongs-en
30.71
12.18
33.51
N/A
N/A
14.60
EntireSongs-zh
34.86
18.68
23.99
N/A
N/A
13.91
ASR Inference Mode Performance (WER ↓)
Model
Infer. Mode
Librispeech
Fleurs-en
Fleurs-zh
Avg.
Qwen3-ASR-1.7B
Offline
1.63 | 3.38
3.35
2.41
2.69
Streaming
1.95 | 4.51
4.02
2.84
3.33
Qwen3-ASR-0.6B
Offline
2.11 | 4.55
4.39
2.88
3.48
Streaming
2.54 | 6.27
5.38
3.40
4.40
Forced Alignment Benchmarks (AAS ms ↓)
Monotonic-Aligner
NFA
WhisperX
Qwen3-ForcedAligner-0.6B
MFA-Labeled Raw
Chinese
161.1
109.8
-
33.1
English
-
107.5
92.1
37.5
French
-
100.7
145.3
41.7
German
-
122.7
165.1
46.5
Italian
-
142.7
155.5
75.5
Japanese
-
-
-
42.2
Korean
-
-
-
37.2
Portuguese
-
-
-
38.4
Russian
-
200.7
-
40.2
Spanish
-
124.7
108.0
36.8
Avg.
161.1
129.8
133.2
42.9
MFA-Labeled Concat-300s
Chinese
1742.4
235.0
-
36.5
English
-
226.7
227.2
58.6
French
-
230.6
2052.2
53.4
German
-
220.3
993.4
62.4
Italian
-
290.5
5719.4
81.6
Japanese
-
-
-
81.3
Korean
-
-
-
42.2
Portuguese
-
-
-
50.0
Russian
-
283.3
-
43.0
Spanish
-
240.2
4549.9
39.6
Cross-lingual
-
-
-
34.2
Avg.
1742.4
246.7
2708.4
52.9
Human-Labeled
Raw
49.9
88.6
-
27.8
Raw-Noisy
53.3
89.5
-
41.8
Concat-60s
51.1
86.7
-
25.3
Concat-300s
410.8
140.0
-
24.8
Concat-Cross-lingual
-
-
-
42.5
Avg.
141.3
101.2
-
32.4